Complete and accurate provider data is an important building block of healthcare operations. Yet many organizations struggle to manage and maintain this data despite large investments. It’s no wonder, considering the complexity of provider records and the systems that store them. This blog post will take a closer look at what provider data is, how it is created, stored, and managed, and what challenges arise when this data is incorrect, outdated, or missing.
What is Provider Data Management?
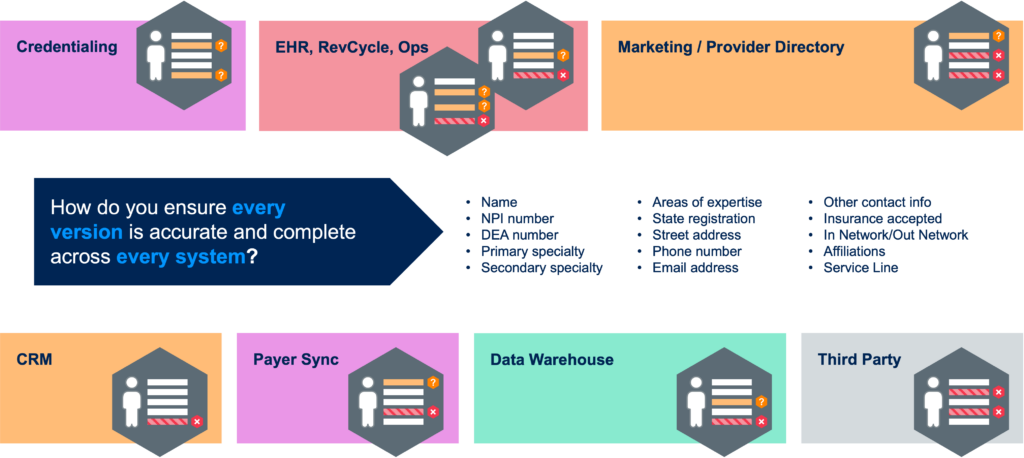
Provider data management (PDM) describes a centralized system that is used to link together and manage provider data across a healthcare organization’s enterprise. The term ‘Manage’ or ‘Management’ in this context means that organizations can centrally adjust, add to, or control provider information that should be used by other applications. A PDM solution is not meant to replace a credentialing application, revenue cycle application, or CRM application – it just ensures the best possible data is being fed into these applications.
Many vendors will use the term PDM to imply any application that allows the creation and management of provider data. Provider data can be created and managed in credentialing systems and CRM applications, and while vendors who offer these solutions might use the term PDM, it is important to distinguish between them and a centralized system that can manage provider data across many different sources and systems.
What is provider data?
Provider data describes details pertaining to both individual practitioners and healthcare organizations including names, addresses, contact information, NPI numbers, IDs and licensing information, and other attributes that are useful in managing healthcare providers. The term ‘practitioner’ is not limited to doctors – it includes nurses, PAs, dentists, chiropractors, and more. Provider organizations include both the locations where people receive care (a clinic, a radiology center, a hospital) and the legal entities that employ practitioners.
Healthcare practitioners have two types of attributes: Information that is useful to uniquely identify and match them, and information that has other value to business operations. The former includes names, addresses, phone numbers, NPI numbers, and other identifiers such as state license IDs, DEA IDs or other Medicare and Medicaid IDs. The latter, also called payload information, includes application-specific IDs, credential information, specialties, education, languages spoken, accepted insurance networks, relationship data, and more. While these attributes wouldn’t be used to identify an individual provider, it is information that is useful for organizations to view in one place.
Relationship details are especially useful to manage practitioners and see available resources. Provder relationships include practitioner-to-practice locations, which include where a provider practices, refers to, and has admitting privileges; practitioner-to-legal organization relationships, which detail where a provider is employed, affiliated with, or an owner of; and organization-to-organization relationships, which state ownership, referrals, and joint venture partners.
What is provider data maintenance?
Provider data maintenance is the consistent reviewing, updating, and correcting of provider data in a provider data management system. While provider data management refers to the bigger picture of organizing data, provider data maintenance refers to the continued upkeep of provider identities in the PDM solution to ensure accuracy and accessibility.
To maintain and manage provider data consistently, an overarching data governance framework should be in place. Data governance describes the rules, procedures, and structures that ensure data is available, correct, and consistent across a healthcare organization. Without such a framework in place, it is much more difficult to keep data up to date, harness its business value, and ensure processes are working efficiently.
A PDM solution that enables timely and effective provider data management and maintenance empowers data stewardship teams to concentrate on other data governance initiatives instead of getting caught up in excessive manual stewardship. Verato’s native Referential Matching makes most matches automatically, but also has workflows to streamline manually resolving any close matches and supports ad-hoc data stewardship when needed. Verato Smart Views, which can include Verato reference data, are composite views that can be configured to deliver the right provider identity data for every use case.
What is a provider data management system?
A provider data management system allows users to create, update, consolidate, analyze, and view provider data across a healthcare enterprise in one place. Healthcare applications that create and use provider data include EHR systems, credential applications, self-scheduling portals, marketing solutions, and many others. Since most of these systems are not interacting with each other, this results in siloed data. As such, there is also little to no ability to ensure that the data is consistent between systems.
A PDM system serves as the single source of truth for provider data. Any new, updated, or deleted provider data is immediately synchronized to the PDM system, either because the changes are made directly in the system, or because they are made in other data-driven applications which use a proactive integration/search that leverages the PDM system. This eliminates uncertainty of data accuracy when looking for information on a certain provider. A PDM solution is also a place where organizations can view, enter, and update information about provider-to-provider relationships.
When searching for a PDM system, healthcare organizations should pay close attention to the accuracy of the solution, its ability to seamlessly connect to existing data sources, high security standards to comply with healthcare regulations, and a cloud-hosted approach for quick deployment and easy updates.
What data challenges does a PDM solution solve?
Issues with provider data are manifold and lead to problems ranging from subpar patient experience to inefficient use of organization resources. Data challenges include missing data that might be available in one system but not another, or information that is not in any system but could be obtained from a third party. Other challenges include inconsistent data, such as different formats of license IDs, titles, and specialties, and outdated data caused by changes in practice locations and affiliations, license, and accreditation renewals. Incorrect data, which can be caused by typos, incorrect practice locations, and mixed-up NPI numbers, is another source of issues. Information that has been acquired from third parties can be especially taxing to clean, reconcile, and manage. A PDM solution that makes it easier to manage this type of data can save hours of manual labor and allow resources to be utilized more efficiently.
A PDM system makes it easier to spot these problems and can help solve them, e.g., by identifying two practitioner records as the same person despite typos in one record or updating a provider in one central system instead of having to do it across multiple applications. A PDM solution that makes it easy to improve existing provider data with data enrichment helps organizations get ahead of some of these challenges.
What business challenges does a PDM solution solve?
A provider data management solution can solve many business challenges typical for healthcare organizations. Incorrect data can cause a slow-down of operations. For example, results or notes can be routed to the wrong person, claims can be rejected due to incorrect coding based on incorrect taxonomy or credential information, or staff members could have to spend time on manually fixing data errors and inconsistencies. Many of these challenges also contribute to poor patient experience, such as incorrect billing or denied claims, which in turn can cause poor provider satisfaction. They can also lead to delayed diagnoses if the care team doesn’t receive results or notes, and frustrations when self-scheduling services do not work correctly.
By employing a provider data management solution, healthcare organizations can resolve data errors and inconsistencies before they become an issue that affects business operations. It also supports provider relationship management, system growth, and strategic planning efforts. Organizations can access comprehensive, up-to-date provider data for outreach and recruitment efforts, understand real-time analytics and insights before, during, and after mergers and acquisitions, and identify overlap of providers networks and redundancy in provider identity data.
Verato Provider Data Management, part of the Verato Universal Identity platform, is powered by Verato Referential Matching and offers the industry’s highest matching accuracy. As a cloud-native service, it is quick to deploy, seamlessly connects to existing applications, and offers a low TCO.
Learn more about Verato Provider Data Management or book a strategy session.
